Init 1
Sol - An MQTT broker from scratch. Part 4 - Data structures
posted on 2019 Mar 07Before proceeding to the implementation of all command handlers, we’re going to design and implement some of the most common data structures needed to the correct functioning of the server, namely hashtable, list and a trie. The last one, being not strictly necessary at this point of the development, will be crucial to manage the abstraction named topic.
Maybe all these data structures are a bit of an overkill for such a low-size project, but I like to have generic containers and data structures available when I start a project longer than a bunch of lines, for convenience and for future increments and implementations where they could come handy. And of course, there’s the learning and exploration side of this activity which I found very valuable.
Let’s start with a simple hashtable, essentially an array that uses a hashing function to obtain a valid index to store our information, trying to minimize the collisions (e.g. keys that compute to the same hash resulting in an already taken index in the array) as much as possible.
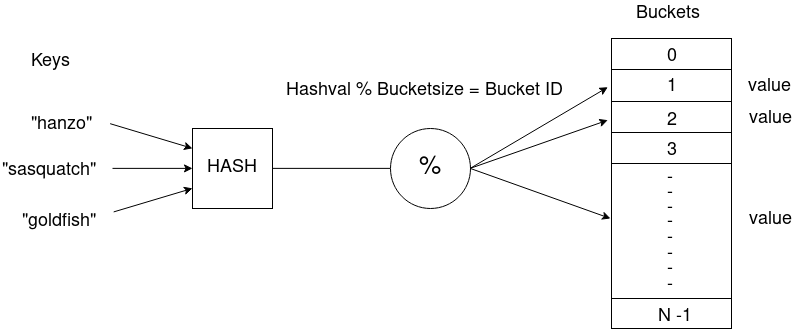
Buckets is the array, usually dynamic, which will store the information associated to the keys.
src/hashtable.h
#ifndef HASHTABLE_H
#define HASHTABLE_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define HASHTABLE_OK 0
#define HASHTABLE_ERR 1
#define HASHTABLE_OOM 2
#define HASHTABLE_FULL 3
/* We need to keep keys and values */
struct hashtable_entry {
const char *key;
void *val;
bool taken;
};
/*
* An HashTable has some maximum size and current size, as well as the data to
* hold.
*/
typedef struct hashtable HashTable;
/*
* HashTable API to create a new `HashTable`, it require a function pointer to
* define a custom destructor, which can be NULL in case of bytes stream or
* simple pointers as values
*/
HashTable *hashtable_create(int (*destructor)(struct hashtable_entry *));
/* Destroy the hashtable by calling functor `destructor` on every
* `struct hashtable_entry`, thus it needs to have a defined destructor function
* for each different data-type inserted. In case of a NULL destructor, it' ll call
* normal free.
*/
void hashtable_release(HashTable *);
/* Return hashtable size */
size_t hashtable_size(const HashTable *);
/* Check if a key is already stored in the hashtable */
int hashtable_exists(HashTable *, const char *);
/*
* Insert a new key-value pair into the hashtable, accept a const char * as
* key and a void * for value
*/
int hashtable_put(HashTable *, const char *, void *);
/* Retrieve a value from the hashtable, accept a const char * as key. */
void *hashtable_get(HashTable *, const char *);
/* Remove a key-value pair from the hashtable, accept a const char * as key. */
int hashtable_del(HashTable *, const char *);
/*
* Iterate through all key-value pairs in the hashtable, accept a functor as
* parameter to apply function to each pair
*/
int hashtable_map(HashTable *, int (*func)(struct hashtable_entry *));
/*
* Iterate through all key-value pairs in the hashtable, accept a functor as
* parameter to apply function to each pair with an additional parameter
*/
int hashtable_map2(HashTable *,
int (*func)(struct hashtable_entry *, void *), void *);
#endif
We define some sort of encapsulation by defining the structure in the source file instead of the header, this way it will be only accessible through functions (like methods in a class).
src/hashtable.c
// -- Omitted includes
/* Hashtable definition */
struct hashtable {
size_t table_size;
size_t size;
int (*destructor)(struct hashtable_entry *);
struct hashtable_entry *entries;
};
const int INITIAL_SIZE = 4;
const int MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH = 8;
const unsigned long KNUTH_PRIME = 2654435761;
static unsigned long crc32(const uint8_t *, unsigned int);
/*
* Hashing function for a string
*/
static uint64_t hashtable_hash_int(HashTable *m, const uint8_t *keystr) {
assert(m && keystr);
uint64_t key = crc32(keystr, strlen((const char *) keystr));
/* Robert Jenkins' 32 bit Mix Function */
key += (key << 12);
key ^= (key >> 22);
key += (key << 4);
key ^= (key >> 9);
key += (key << 10);
key ^= (key >> 2);
key += (key << 7);
key ^= (key >> 12);
/* Knuth's Multiplicative Method */
key = (key >> 3) * KNUTH_PRIME;
return key % m->table_size;
}
/*
* Return the integer of the location in entries to store the point to the item
* or -HASHTABLE_FULL.
*/
static int hashtable_hash(HashTable *table, const uint8_t *key) {
assert(table && key);
/* If full, return immediately */
if (table->size >= (table->table_size / 2))
return -HASHTABLE_FULL;
/* Find the best index */
uint64_t curr = hashtable_hash_int(table, key);
char *k, *currk;
/* Linear probing */
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH; i++) {
if (table->entries[curr].taken == false)
return curr;
k = (char *) table->entries[curr].key;
currk = (char *) key;
if (table->entries[curr].taken == true &&
STREQ(k, currk, strlen(k)) == true)
return curr;
curr = (curr + 1) % table->table_size;
}
return -HASHTABLE_FULL;
}
/*
* Doubles the size of the hashtable, and rehashes all the elements
*/
static int hashtable_rehash(HashTable *table) {
assert(table);
size_t old_size;
struct hashtable_entry *curr;
/* Setup the new elements */
struct hashtable_entry *temp =
calloc(2 * table->table_size, sizeof(*temp));
if (!temp)
return -HASHTABLE_ERR;
/* Update the array */
curr = table->entries;
table->entries = temp;
/* Update the size */
old_size = table->table_size;
table->table_size = 2 * table->table_size;
table->size = 0;
int status;
/* Rehash the elements */
for (size_t i = 0; i < old_size; i++) {
if (curr[i].taken == false)
continue;
if ((status = hashtable_put(table, curr[i].key,
curr[i].val)) != HASHTABLE_OK)
return status;
}
free(curr);
return HASHTABLE_OK;
}
/* callback function used with iterate to clean up the hashtable */
static int destroy_entry(struct hashtable_entry *entry) {
if (!entry)
return -HASHTABLE_ERR;
// free key field
if (entry->key)
free((void *) entry->key);
// free value field
if (entry->val)
free(entry->val);
return HASHTABLE_OK;
}
/*
* Return an empty hashtable, or NULL on failure. The newly create HashTable is
* dynamically allocated on the heap memory, so it must be released manually.
*/
HashTable *hashtable_create(int (*destructor)(struct hashtable_entry *)) {
HashTable *table = malloc(sizeof(HashTable));
if(!table)
return NULL;
table->entries = calloc(INITIAL_SIZE, sizeof(struct hashtable_entry));
if(!table->entries) {
hashtable_release(table);
return NULL;
}
table->destructor = destructor ? destructor : destroy_entry;
table->table_size = INITIAL_SIZE;
table->size = 0;
return table;
}
size_t hashtable_size(const HashTable *table) {
return table->size;
}
int hashtable_exists(HashTable *table, const char *key) {
void *ret = hashtable_get(table, key);
return !ret ? 0 : 1;
}
/* Add a new key-value pair into the hashtable entries array, use chaining in
case of collision. */
int hashtable_put(HashTable *table, const char *key, void *val) {
assert(table && key);
/* Find a place to put our value */
int index = hashtable_hash(table, (const uint8_t *) key);
while (index == -HASHTABLE_FULL){
if (hashtable_rehash(table) == -HASHTABLE_ERR)
return -HASHTABLE_ERR;
index = hashtable_hash(table, (const uint8_t *) key);
}
/* Set the entries */
table->entries[index].val = val;
table->entries[index].key = key;
/* Update taken flag, if it was false, update the size also */
if (table->entries[index].taken == false) {
table->entries[index].taken = true;
table->size++;
}
return HASHTABLE_OK;
}
/*
* Get the value void pointer out of the hashtable associated to a key
*/
void *hashtable_get(HashTable *table, const char *key) {
assert(table && key);
/* Find data location */
uint64_t curr = hashtable_hash_int(table, (const uint8_t *) key);
/* Linear probing, if necessary */
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH; i++){
if (table->entries[curr].taken == true) {
if (STREQ(table->entries[curr].key, key, strlen(key)) == true)
return table->entries[curr].val;
}
curr = (curr + 1) % table->table_size;
}
/* Not found */
return NULL;
}
/*
* Remove an element with that key from the hashtable
*/
int hashtable_del(HashTable *table, const char *key) {
assert(table && key);
/* Find key */
uint64_t curr = hashtable_hash_int(table, (const uint8_t *) key);
/* Linear probing, if necessary */
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH; i++) {
// check wether the position in array is in use
if (table->entries[curr].taken == true) {
if (STREQ(table->entries[curr].key, key, strlen(key)) == true) {
/* Blank out the fields */
table->entries[curr].taken = false;
/* Reduce the size */
table->size--;
/* Destroy the entry */
table->destructor(&table->entries[curr]);
return HASHTABLE_OK;
}
}
curr = (curr + 1) % table->table_size;
}
/* Data not found */
return -HASHTABLE_ERR;
}
/*
* Iterate the function parameter over each element in the hashmap. The unique
* void * argument is passed to the function as its first argument,
* representing the key-value pair structure.
*/
int hashtable_map(HashTable *table, int (*func)(struct hashtable_entry *)) {
assert(func);
/* On empty hashmap, return immediately */
if (!table || table->size <= 0)
return -HASHTABLE_ERR;
/* Linear probing */
for (size_t i = 0; i < table->table_size; i++) {
if (table->entries[i].taken == true) {
/* Apply function to the key-value entry */
struct hashtable_entry data = table->entries[i];
int status = func(&data);
if (status != HASHTABLE_OK)
return status;
}
}
return HASHTABLE_OK;
}
/*
* Iterate through all key-value pairs in the hashtable, accept a functor as
* parameter to apply function to each pair with an additional parameter
*/
int hashtable_map2(HashTable *table,
int (*func)(struct hashtable_entry *, void *),
void *param) {
assert(func);
/* On empty hashmap, return immediately */
if (!table || table->size <= 0)
return -HASHTABLE_ERR;
/* Linear probing */
for (size_t i = 0; i < table->table_size; i++) {
if (table->entries[i].taken == true) {
/* Apply function to the key-value entry */
struct hashtable_entry data = table->entries[i];
int status = func(&data, param);
if (status != HASHTABLE_OK)
return status;
}
}
return HASHTABLE_OK;
}
/*
* De-allocate the hashtable using the defined destructor, if the destructor is
* NULL it call normal free on key-value pairs.
*/
void hashtable_release(HashTable *table){
if (!table)
return;
hashtable_map(table, table->destructor);
if (!table || !table->entries)
return;
free(table->entries);
free(table);
}
/* The implementation here was originally done by Gary S. Brown. Slightly
* modified by Pete Warden, without any imposition on the reuse of the code.
*/
/* ============================================================= */
/* COPYRIGHT (C) 1986 Gary S. Brown. You may use this program, or */
/* code or tables extracted from it, as desired without restriction. */
/* */
/* First, the polynomial itself and its table of feedback terms. The */
/* polynomial is */
/* X^32+X^26+X^23+X^22+X^16+X^12+X^11+X^10+X^8+X^7+X^5+X^4+X^2+X^1+X^0 */
/* */
/* Note that we take it "backwards" and put the highest-order term in */
/* the lowest-order bit. The X^32 term is "implied"; the LSB is the */
/* X^31 term, etc. The X^0 term (usually shown as "+1") results in */
/* the MSB being 1. */
/* */
/* Note that the usual hardware shift register implementation, which */
/* is what we're using (we're merely optimizing it by doing eight-bit */
/* chunks at a time) shifts bits into the lowest-order term. In our */
/* implementation, that means shifting towards the right. Why do we */
/* do it this way? Because the calculated CRC must be transmitted in */
/* order from highest-order term to lowest-order term. UARTs transmit */
/* characters in order from LSB to MSB. By storing the CRC this way, */
/* we hand it to the UART in the order low-byte to high-byte; the UART */
/* sends each low-bit to high-bit; and the result is transmission bit */
/* by bit from highest- to lowest-order term without requiring any bit */
/* shuffling on our part. Reception works similarly. */
/* */
/* The feedback terms table consists of 256, 32-bit entries. Notes: */
/* */
/* The table can be generated at runtime if desired; code to do so */
/* is shown later. It might not be obvious, but the feedback */
/* terms simply represent the results of eight shift/xor opera- */
/* tions for all combinations of data and CRC register values. */
/* */
/* The values must be right-shifted by eight bits by the "updcrc" */
/* logic; the shift must be unsigned (bring in zeroes). On some */
/* hardware you could probably optimize the shift in assembler by */
/* using byte-swap instructions. */
/* polynomial $edb88320 */
/* */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------- */
static unsigned long crc32_tab[] = {
0x00000000L, 0x77073096L, 0xee0e612cL, 0x990951baL, 0x076dc419L,
0x706af48fL, 0xe963a535L, 0x9e6495a3L, 0x0edb8832L, 0x79dcb8a4L,
0xe0d5e91eL, 0x97d2d988L, 0x09b64c2bL, 0x7eb17cbdL, 0xe7b82d07L,
0x90bf1d91L, 0x1db71064L, 0x6ab020f2L, 0xf3b97148L, 0x84be41deL,
0x1adad47dL, 0x6ddde4ebL, 0xf4d4b551L, 0x83d385c7L, 0x136c9856L,
0x646ba8c0L, 0xfd62f97aL, 0x8a65c9ecL, 0x14015c4fL, 0x63066cd9L,
0xfa0f3d63L, 0x8d080df5L, 0x3b6e20c8L, 0x4c69105eL, 0xd56041e4L,
0xa2677172L, 0x3c03e4d1L, 0x4b04d447L, 0xd20d85fdL, 0xa50ab56bL,
0x35b5a8faL, 0x42b2986cL, 0xdbbbc9d6L, 0xacbcf940L, 0x32d86ce3L,
0x45df5c75L, 0xdcd60dcfL, 0xabd13d59L, 0x26d930acL, 0x51de003aL,
0xc8d75180L, 0xbfd06116L, 0x21b4f4b5L, 0x56b3c423L, 0xcfba9599L,
0xb8bda50fL, 0x2802b89eL, 0x5f058808L, 0xc60cd9b2L, 0xb10be924L,
0x2f6f7c87L, 0x58684c11L, 0xc1611dabL, 0xb6662d3dL, 0x76dc4190L,
0x01db7106L, 0x98d220bcL, 0xefd5102aL, 0x71b18589L, 0x06b6b51fL,
0x9fbfe4a5L, 0xe8b8d433L, 0x7807c9a2L, 0x0f00f934L, 0x9609a88eL,
0xe10e9818L, 0x7f6a0dbbL, 0x086d3d2dL, 0x91646c97L, 0xe6635c01L,
0x6b6b51f4L, 0x1c6c6162L, 0x856530d8L, 0xf262004eL, 0x6c0695edL,
0x1b01a57bL, 0x8208f4c1L, 0xf50fc457L, 0x65b0d9c6L, 0x12b7e950L,
0x8bbeb8eaL, 0xfcb9887cL, 0x62dd1ddfL, 0x15da2d49L, 0x8cd37cf3L,
0xfbd44c65L, 0x4db26158L, 0x3ab551ceL, 0xa3bc0074L, 0xd4bb30e2L,
0x4adfa541L, 0x3dd895d7L, 0xa4d1c46dL, 0xd3d6f4fbL, 0x4369e96aL,
0x346ed9fcL, 0xad678846L, 0xda60b8d0L, 0x44042d73L, 0x33031de5L,
0xaa0a4c5fL, 0xdd0d7cc9L, 0x5005713cL, 0x270241aaL, 0xbe0b1010L,
0xc90c2086L, 0x5768b525L, 0x206f85b3L, 0xb966d409L, 0xce61e49fL,
0x5edef90eL, 0x29d9c998L, 0xb0d09822L, 0xc7d7a8b4L, 0x59b33d17L,
0x2eb40d81L, 0xb7bd5c3bL, 0xc0ba6cadL, 0xedb88320L, 0x9abfb3b6L,
0x03b6e20cL, 0x74b1d29aL, 0xead54739L, 0x9dd277afL, 0x04db2615L,
0x73dc1683L, 0xe3630b12L, 0x94643b84L, 0x0d6d6a3eL, 0x7a6a5aa8L,
0xe40ecf0bL, 0x9309ff9dL, 0x0a00ae27L, 0x7d079eb1L, 0xf00f9344L,
0x8708a3d2L, 0x1e01f268L, 0x6906c2feL, 0xf762575dL, 0x806567cbL,
0x196c3671L, 0x6e6b06e7L, 0xfed41b76L, 0x89d32be0L, 0x10da7a5aL,
0x67dd4accL, 0xf9b9df6fL, 0x8ebeeff9L, 0x17b7be43L, 0x60b08ed5L,
0xd6d6a3e8L, 0xa1d1937eL, 0x38d8c2c4L, 0x4fdff252L, 0xd1bb67f1L,
0xa6bc5767L, 0x3fb506ddL, 0x48b2364bL, 0xd80d2bdaL, 0xaf0a1b4cL,
0x36034af6L, 0x41047a60L, 0xdf60efc3L, 0xa867df55L, 0x316e8eefL,
0x4669be79L, 0xcb61b38cL, 0xbc66831aL, 0x256fd2a0L, 0x5268e236L,
0xcc0c7795L, 0xbb0b4703L, 0x220216b9L, 0x5505262fL, 0xc5ba3bbeL,
0xb2bd0b28L, 0x2bb45a92L, 0x5cb36a04L, 0xc2d7ffa7L, 0xb5d0cf31L,
0x2cd99e8bL, 0x5bdeae1dL, 0x9b64c2b0L, 0xec63f226L, 0x756aa39cL,
0x026d930aL, 0x9c0906a9L, 0xeb0e363fL, 0x72076785L, 0x05005713L,
0x95bf4a82L, 0xe2b87a14L, 0x7bb12baeL, 0x0cb61b38L, 0x92d28e9bL,
0xe5d5be0dL, 0x7cdcefb7L, 0x0bdbdf21L, 0x86d3d2d4L, 0xf1d4e242L,
0x68ddb3f8L, 0x1fda836eL, 0x81be16cdL, 0xf6b9265bL, 0x6fb077e1L,
0x18b74777L, 0x88085ae6L, 0xff0f6a70L, 0x66063bcaL, 0x11010b5cL,
0x8f659effL, 0xf862ae69L, 0x616bffd3L, 0x166ccf45L, 0xa00ae278L,
0xd70dd2eeL, 0x4e048354L, 0x3903b3c2L, 0xa7672661L, 0xd06016f7L,
0x4969474dL, 0x3e6e77dbL, 0xaed16a4aL, 0xd9d65adcL, 0x40df0b66L,
0x37d83bf0L, 0xa9bcae53L, 0xdebb9ec5L, 0x47b2cf7fL, 0x30b5ffe9L,
0xbdbdf21cL, 0xcabac28aL, 0x53b39330L, 0x24b4a3a6L, 0xbad03605L,
0xcdd70693L, 0x54de5729L, 0x23d967bfL, 0xb3667a2eL, 0xc4614ab8L,
0x5d681b02L, 0x2a6f2b94L, 0xb40bbe37L, 0xc30c8ea1L, 0x5a05df1bL,
0x2d02ef8dL
};
/* Return a 32-bit CRC of the contents of the buffer. */
static unsigned long crc32(const uint8_t *s, unsigned int len) {
unsigned int i;
uint64_t crc32val;
crc32val = 0LL;
for (i = 0; i < len; i ++) {
crc32val = crc32_tab[(crc32val ^ s[i]) & 0xff] ^ (crc32val >> 8);
}
return crc32val;
}
Our hash function just compute the CRC32 of a given string, using the Knuth multiplicative method, another valid hash could be the Murmur3, but I won’t analyze the best algorithms and implementations around that best work for key hashing.
We’ll surely gonna need a list as well, vector could be more performant by leveraging his cache-friendly nature, but the gain is not so high for what we’re going to do, O(1) in insertion will be good enough for our use-cases. Our sequential container will be based on a singly-linked list, with a pointer to head and tail, this way we ensure O(1) for insertion on either sides.
src/list.h
#ifndef LIST_H
#define LIST_H
struct list_node {
void *data;
struct list_node *next;
};
typedef struct list {
struct list_node *head;
struct list_node *tail;
unsigned long len;
int (*destructor)(struct list_node *);
} List;
/*
* Compare function, accept two void * arguments, generally referring a node
* and his subsequent
*/
typedef int (*compare_func)(void *, void *);
/* Create an empty list */
List *list_create(int (*destructor)(struct list_node*));
/*
* Release a list, accept a integer flag to control the depth of the free call
* (e.g. going to free also data field of every node)
*/
void list_release(List *, int);
/* Return list size */
unsigned long list_size(const List *);
/* Clear out the list without de-allocating it */
void list_clear(List *, int);
/* Insert data into a node and push it to the front of the list */
List *list_push(List *, void *);
/* Insert data into a node and push it to the back of the list */
List *list_push_back(List *, void *);
/*
* Remove a node from the list based on a compare function that must be
* previously defined and passed in as a function pointer, accept two void
* *args, which generally means a node and his subsequent
*/
void list_remove(List *, struct list_node *, compare_func);
/*
* Remove a single node from the list, the first one satisfy compare_func
* criteria, without de-allocating it
*/
struct list_node *list_remove_node(List *, void *, compare_func);
/* Comapare function for merge_sort application */
typedef int cmp(void *, void *);
/* Insert a new node into a list while maintaining the order of the elements */
struct list_node *list_sort_insert(struct list_node **,
struct list_node *, compare_func);
/* Divide a list in 2 sublists at roughly the middle of the original list */
struct list_node *bisect_list(struct list_node *);
#endif
src/list.c
#include "list.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
static struct list_node *list_node_remove(struct list_node *,
struct list_node *,
compare_func, int *);
/*
* Create a list, initializing all fields
*/
List *list_create(int (*destructor)(struct list_node *)) {
List *l = malloc(sizeof(List));
if (!l)
return NULL;
// set default values to the List structure fields
l->head = l->tail = NULL;
l->len = 0L;
// TODO if NULL set default destructor
l->destructor = destructor;
return l;
}
/*
* Destroy a list, releasing all allocated memory
*/
void list_release(List *l, int deep) {
if (!l)
return;
struct list_node *h = l->head;
struct list_node *tmp;
// free all nodes
while (l->len--) {
tmp = h->next;
if (l->destructor)
l->destructor(h);
else {
if (h) {
if (h->data && deep == 1)
free(h->data);
free(h);
}
}
h = tmp;
}
// free List structure pointer
free(l);
}
unsigned long list_size(const List *list) {
return list->len;
}
/*
* Destroy a list, releasing all allocated memory but the list itself
*/
void list_clear(List *l, int deep) {
if (!l || !l->head)
return;
struct list_node *h = l->head;
struct list_node *tmp;
// free all nodes
while (l->len--) {
tmp = h->next;
if (h) {
if (h->data && deep == 1)
free(h->data);
free(h);
}
h = tmp;
}
l->head = l->tail = NULL;
l->len = 0L;
}
/*
* Insert value at the front of the list
* Complexity: O(1)
*/
List *list_push(List *l, void *val) {
struct list_node *new_node = malloc(sizeof(struct list_node));
if (!new_node)
return NULL;
new_node->data = val;
if (l->len == 0) {
l->head = l->tail = new_node;
new_node->next = NULL;
} else {
new_node->next = l->head;
l->head = new_node;
}
l->len++;
return l;
}
/*
* Insert value at the back of the list
* Complexity: O(1)
*/
List *list_push_back(List *l, void *val) {
struct list_node *new_node = malloc(sizeof(struct list_node));
if (!new_node)
return NULL;
new_node->data = val;
new_node->next = NULL;
if (l->len == 0) {
l->head = l->tail = new_node;
} else {
l->tail->next = new_node;
l->tail = new_node;
}
l->len++;
return l;
}
void list_remove(List *l, struct list_node *node, compare_func cmp) {
if (!l || !node)
return;
int counter = 0;
l->head = list_node_remove(l->head, node, cmp, &counter);
l->len -= counter;
}
static struct list_node *list_node_remove(struct list_node *head,
struct list_node *node,
compare_func cmp, int *counter) {
if (!head)
return NULL;
if (cmp(head, node) == 0) {
struct list_node *tmp_next = head->next;
free(head);
head = NULL;
// Update remove counter
(*counter)++;
return tmp_next;
}
head->next = list_node_remove(head->next, node, cmp, counter);
return head;
}
static struct list_node *list_remove_single_node(struct list_node *head,
void *data,
struct list_node **ret,
compare_func cmp) {
if (!head)
return NULL;
// We want the first match
if (cmp(head, data) == 0 && !*ret) {
struct list_node *tmp_next = head->next;
*ret = head;
return tmp_next;
}
head->next = list_remove_single_node(head->next, data, ret, cmp);
return head;
}
struct list_node *list_remove_node(List *list, void *data, compare_func cmp) {
if (list->len == 0 || !list)
return NULL;
struct list_node *node = NULL;
list_remove_single_node(list->head, data, &node, cmp);
if (node) {
list->len--;
node->next = NULL;
}
return node;
}
/* Insert a new list node in a list maintaining the order of the list */
struct list_node *list_sort_insert(struct list_node **head,
struct list_node *new, cmp cmp_func) {
if (!*head || cmp_func(*head, new) >= 0) {
new->next = *head;
*head = new;
} else {
struct list_node *cur;
cur = *head;
while (cur->next && cmp_func(cur->next, new) < 0)
cur = cur->next;
new->next = cur->next;
cur->next = new;
}
return *head;
}
/*
* Returns a pointer to a node near the middle of the list,
* after having truncated the original list before that point.
*/
struct list_node *bisect_list(struct list_node *head) {
/* The fast pointer moves twice as fast as the slow pointer. */
/* The prev pointer points to the node preceding the slow pointer. */
struct list_node *fast = head, *slow = head, *prev = NULL;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
fast = fast->next->next;
prev = slow;
slow = slow->next;
}
if (prev != NULL)
prev->next = NULL;
return slow;
}
We have successfully implemented two classic data structures that offer useful features to our project:
- hashtable
- list
The next structure must be something that allow us to easily manage the topics
and their hierarchical nature.
Part 5 will focus
on a tree implementation that provide exactly what we need.
Categories: #c #unix #tutorial #structures